Will the robot really feel?
In our last news article, we mentioned how the iRobot PackBot will soon be acquiring a sense of touch. Actually, it won’t be the PackBot that will be endowed with this sensation; rather, it will be the soldier controlling the robot.
In case you’re not familiar with the iRobot PackBot, you may click that link to watch a music video featuring the numero uno robot on the battlefield. iRobot PackBots are usually employed to assist soldiers in bomb disposal and reconnaissance missions. These robots are not fully autonomous though. They’re remotely controlled by soldiers using joystick-like controllers.

We’re not sure whether the future controllers will still look like the present ones. What we’re sure of is that they will be driven by haptic technology. Haptic technology allows users to receive haptic or force feedbacks when handling the controllers. That is, the controllers will exert resistant forces and vibrations that are in sync with what the user sees on a display.
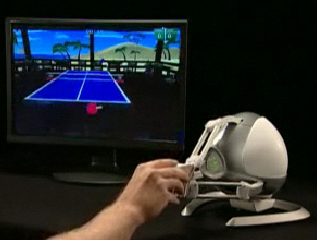 In the case of the PackBot, iRobot will be working with Novint Technologies, the company responsible for the haptic-driven control used in certain video games. The video game controller, called the Novint Falcon, is equipped with electrical motors that provide tactile feedback.
In the case of the PackBot, iRobot will be working with Novint Technologies, the company responsible for the haptic-driven control used in certain video games. The video game controller, called the Novint Falcon, is equipped with electrical motors that provide tactile feedback.
For example, when using the Novint Falcon to lift an object, you can actually distinguish a heavy object from a lighter one based on the amount of resisting force the Falcon’s handle gives off. Another example is an accessory for the Novint Falcon, called the Pistol Grip (and well, shaped like a pistol – see image below), which will make you feel the gun’s recoil every time you pull the trigger.
 The PackBot project is not the first time that Novint Technologies will be working with the military. Last month, they were awarded a subcontract to develop a physical rehabilitation game for soldiers suffering from traumatic brain injury or TBI. Through an interactive game and haptic technology, patients will be able to perform rehabilitative tasks.
The PackBot project is not the first time that Novint Technologies will be working with the military. Last month, they were awarded a subcontract to develop a physical rehabilitation game for soldiers suffering from traumatic brain injury or TBI. Through an interactive game and haptic technology, patients will be able to perform rehabilitative tasks.
For example, a patient suffering from TBI may not be able to control his hand movement. By establishing spatial limitations on the patient’s arm movements as he tries to handle a virtual object on the screen, can improve the patient’s accuracy. By integrating this sense of touch in a game, soldiers who have lost their sight or hearing can also benefit from it.
The main difference between previous projects and that on the iRobot PackBot is in the kind of objects the user will be handling through the controller – the previous projects made use of virtual objects while this one will be making use of real ones, such as a rock or even a bomb.


